In the dynamic realm of scientific research, laboratories are hubs of innovation, discovery, and meticulous experimentation. The efficiency and success of these endeavors heavily depend on the utilization of cutting-edge tools and equipment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the top 20 lab equipment that forms the backbone of diverse scientific disciplines, encompassing biology, chemistry, physics, and beyond.
Table of Contents
Vertical Laminar Flow Hood:
- Vertical laminar flow hoods create a controlled, sterile environment by directing air through a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter. These hoods are crucial for tasks requiring aseptic conditions, such as cell culture and sample preparation, ensuring that contaminants are kept at bay.
Lab Coat:
- Lab coats are not merely uniforms; they are essential protective garments. They shield researchers from chemical splashes, biological contaminants, and other hazards. Lab coats are a fundamental element of laboratory safety and lab equipment, promoting a secure working environment.
Bunsen Burners:
- Bunsen burners are classic heating devices used for a variety of purposes, including sterilization, flame tests, and heating solutions. They provide a controlled and easily adjustable flame, making them a staple in chemistry laboratories.
Filter Paper:
- Filter paper is a porous lab equipment used to separate solids from liquids or gasses. Its permeability allows the passage of liquids while retaining particles, making it an invaluable tool in filtration processes across various scientific applications.

Lab Notebook:
- The lab notebook is the researcher’s documentation hub. It serves as a detailed record of experimental procedures, observations, and results. A well-maintained lab notebook is essential for reproducibility, collaboration, and maintaining a scientific record.
Spatulas:
- Spatulas are versatile lab equipment tools in laboratories, serving to transfer, mix, or manipulate small quantities of substances. Available in various materials, spatulas are indispensable for precise measurement and handling of samples.

Beaker Tongs:
- Beaker tongs provide a safe means of handling hot beakers. Their design allows for a secure grip on beakers of different sizes, facilitating the safe transfer of heated liquids or substances in the laboratory.
Peristaltic Pump:
- Peristaltic pumps employ a pulsating motion to move liquids through tubing. These pumps are commonly used for precise and continuous fluid transfer, ensuring accuracy in various applications, such as chromatography and chemical dispensing.
Electronic Balance:
- Electronic balances is a commonly used lab equipment that offers accurate and rapid measurements of mass. Their digital nature and precision make them essential for quantitative analyses, contributing to the reliability and reproducibility of experimental results.

Analytical Balance:
- Analytical balances are high-precision instruments designed for precise measurement of mass in the sub-milligram range. Widely used in quantitative analysis, they play a critical role in analytical chemistry and pharmaceutical research.
Compound Microscope:
- The compound microscope is a cornerstone of biological research, enabling the observation of microscopic structures. With magnification capabilities, it is indispensable for tasks ranging from cell biology to microbiology.
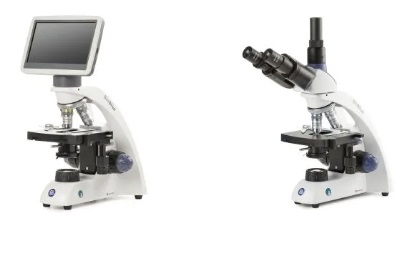
Digital Microscope:
- Digital microscopes combine traditional microscopy with digital imaging technology. They allow researchers to capture, record, and share images digitally, facilitating collaborative research and analysis.
Muffle Furnace:
- Muffle furnaces provide controlled high-temperature environments, often used for tasks like ashing, heat treating, and determining volatile content in samples. These furnaces contribute to material analysis and sample preparation in various fields.

Cryogenic Gloves:
- Cryogenic gloves are specially designed to protect hands when handling materials at extremely low temperatures. In applications involving cryopreservation or working with liquid nitrogen, these gloves safeguard researchers from cold-related hazards.
Dewar Flask:
- Dewar flasks, also known as vacuum flasks or thermos flasks, are crucial for the storage and transportation of cryogenic liquids such as liquid nitrogen. Their double-walled construction minimizes heat transfer, maintaining low temperatures.
Flammable Cabinet:
- Flammable cabinets are safety storage units designed to house flammable liquids and chemicals. Equipped with features like fire-resistant materials and ventilation, they mitigate the risks associated with storing hazardous materials in laboratories.

Petri Dishes:
- Petri dishes are shallow, cylindrical containers with lids, widely used for culturing and observing microorganisms. They provide a controlled environment for microbial growth, crucial in microbiology and other life sciences.
Laboratory Glassware:
- Laboratory glassware encompasses a diverse range, including beakers, flasks, and pipettes. These vessels are fundamental for measuring, mixing, and holding liquids, providing researchers with essential tools for various experimental procedures.
Erlenmeyer Flask:
- Erlenmeyer flasks, with their conical shape and narrow neck, allow for efficient mixing and swirling of liquids. They are commonly used in chemical reactions, titrations, and culture media preparation.

Graduated Cylinders:
- Graduated cylinders are precision measuring instruments used for volume measurements in liquid handling. With graduated markings along their length, these cylinders provide accurate readings for liquids of various viscosities.
In conclusion, these top 20 lab equipment items represent the diverse array of tools that scientists rely on daily in their quest for knowledge. From the foundational safety provided by lab coats to the precision of analytical balances, each piece plays a crucial role in advancing scientific understanding and discovery. As technology continues to advance, these essential tools evolve, ensuring that laboratories remain at the forefront of innovation and discovery.